Many of you may not know about superficial abdominal reflex and abdominal reflex tests. So, in today’s blog, we’ll provide you complete information on these concepts. Even students often search for these terms, so it will be easy for students to understand the full concept. It is suggested that you make sure to fully focus on this concept without skipping anything, and then you can grab more information on it. Let’s get started:
Overview of Abdominal Reflex
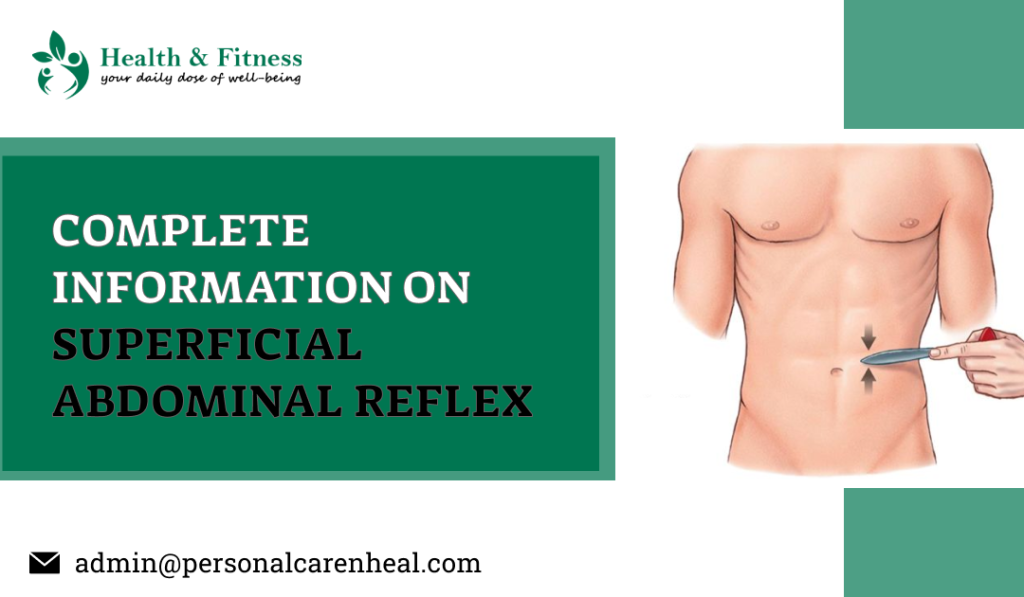
An abdominal reflex is a superficial neurological reflex that is induced by stroking the abdomen around the umbilicus. It helps in determining the CNS lesion level. As a superficial reflex, it is polysynaptic.
Generally, superficial abdominal reflex (SAR) is an essential part of the neurologic assessment. SAR is generally present, but in various pathological and physiological conditions, it may be present or absent. If an abdominal incision is present, then it creates a dilemma in the brain of the clinician for it impacting this reflex.
Requisites for Extraction of Abdominal Reflex
- Massage the abdomen
- Describe the whole procedure to the patients
- Use light non-painful stimulus with compression of the muscle
- The stimulus should be pleasant
Elicitation Method
The patient needs to lie flat, gently massage the abdomen to know the degree of relaxation and skin sensitivity. Then explain the whole procedure to the patient and show it on the chest. With a blunt object, stroke the abdomen from without inwards, stimulate all four quadrants of the abdomen.
Normal Response: There is homolateral compression of the abdominal muscles, and linea alba’s retraction and the umbilicus around the area stimulated.
Abdominal Reflex Root Value
Superficial abdominal reflex center – T7 to T12 spinal parts
Posterior root = Afferent and Anterior root = Efferent
- Lower abdominal: T10-T12
- Mid abdominal: T8-T10
- Upper abdominal: T6-T8
Types of Abdominal Reflex
The following are different types of abdominal reflexes:
- Normal abdominal reflex
- Absent abdominals
- Fatiguable abdominals
- Exaggerated abdominals
- Dissociated abdominals
- Inverted abdominals
Absent abdominal reflex is present in
- Pyramidal tract lesion
It should be present in all cases
- Reflex may be absent because of a break in the reflex arc
- Motor root
- Sensory root
- Peripheral nerve
- Lax abdomen
- Tense abdomen
- Surgery
- Pregnancy
Fatiguable Abdominals
It is present in subtle corticospinal tract lesion
Exaggerated Abdominal Reflex is present in
- Anxiety
- Parkinsonism
Dissociated Abdominals
It can be seen in UMN lesions that the superficial abdominal reflex is not present, but the deep abdominal reflex is exaggerated.
Inverted Abdominal Reflex
In an inverted abdominal reflex, stimulation of the paralysed side of the abdomen causes contraction of the normal side, so the umbilicus turns to that side and the reflex is not present on the weak side.
Fallacies
- Heavy stimulation leads to the elicitation of a deep abdominal reflex that causes exaggerated corticospinal tract lesions.
- A tense or lax abdomen can cause absent abdominals.
- Abdominals are not always absent in several sclerosis.
- Trouble in relaxing the abdominals can be avoided by extracting the jerk while the person lies upright.
- If it is a lax abdomen, slight contraction can be extracted by stimulation around the ribs and inguinal ligament.
If you are facing abdominal pain, then you can opt for an abdominal reflex test.
What is Abdominal Pain?
Many of you may face abdominal pain between the pelvic region and chest. Abdominal pain can be achy, sharp, crampy, or intermittent. It is also known as stomach pain. Diseases or inflammation can impact organs in the abdomen and cause abdominal pain. The organs that are located in the abdomen:
- Kidneys
- Stomach
- Liver
- Pancreas
- Appendix
- Intestines
- Spleen
- Gallbladder
Bacterial, viral, or parasitic infections can affect the intestines and stomach that can lead to abdominal pain.
Abdominal Pain Causes
Many conditions can cause abdominal pain. However, the main cause can be abnormal growths, infection, obstruction, inflammation, and intestinal disorders. When you have infections in the throat, blood, or intestines, then they can enter your digestive tract that can cause abdominal pain. These infections can also result in changes in digestion, such as constipation or diarrhea.
Other common reasons for abdominal pain:
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Vomiting
- Stress
- Gastroenteritis
- Acid reflux
Abdominal pain can be categorized as localized, colicky, or cramp-like pain. So, this is the blog that explains what exactly superficial abdominal reflex is and the causes of abdominal pain. If you can’t identify abdominal pain reasons, then you can read all of the above-mentioned points. This blog will clear all you doubts, so read this blog with concentration. We hope you get all the answers to your questions from this blog.


